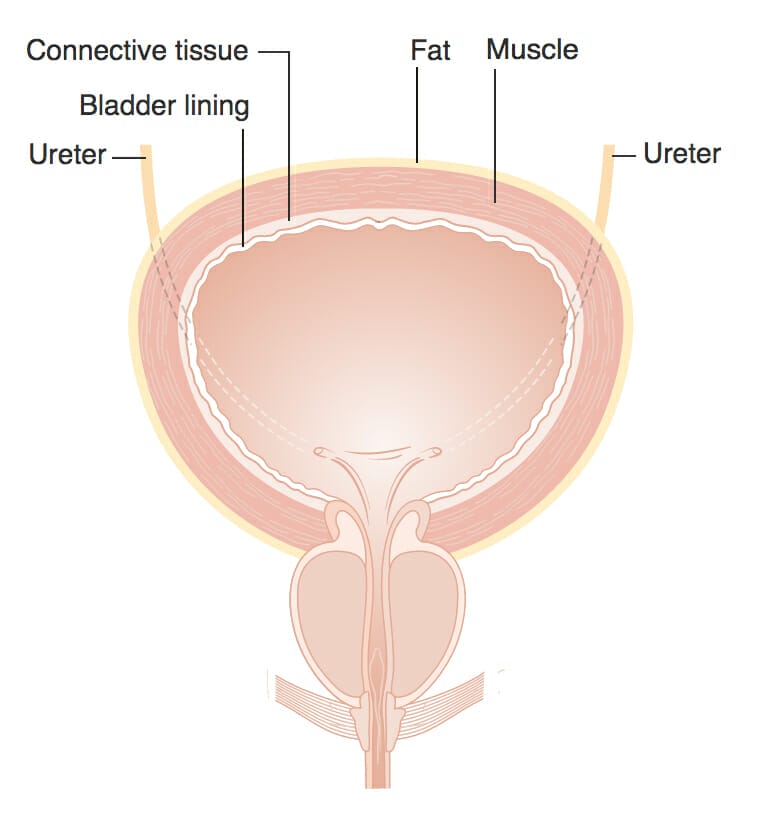
The bladder is a hollow muscular organ that stores urine produced by the kidneys prior to expelling it through the urethra (urination). There are a number of conditions that can affect the bladder.
What is an overactive bladder?
Overactive bladder is a common condition when your bladder contracts suddenly when it is not full. You can pass urine more frequently than normal and there are often sudden urges to pass urine. Sometimes incontinence can result.
How can this be managed?
- Conservative strategies. Dietary and lifestyle changes are often enough to dramatically improve symptoms. These include reducing caffeine, alcohol and acidic drinks. Bladder retraining and pelvic floor physiotherapy can also help significantly.
- Medication. Anticholinergics (such as solifenacin) and Beta-3 agonists (such as mirabegron) are medications that suppress bladder muscle activity, reducing urinary frequency and urgency. Side effects include dry mouth, indigestion and constipation.
- Botox injections. Via a cystoscope, Botox is injected directly into the bladder. This partially paralyses the bladder muscle and usually gives good relief of symptoms. There is 10% risk of urinary retention (temporary) and so intermittent catheterization is sometimes required afterwards.