Prostatitis is a condition when the prostate is affected by infection or inflammation resulting in urinary symptoms.
What is the prostate?
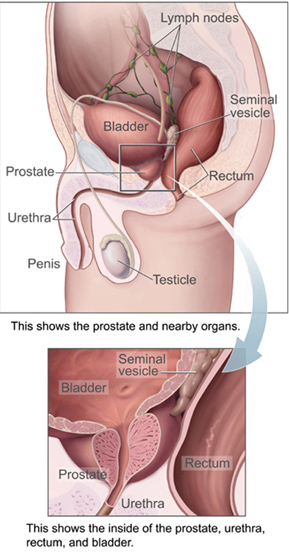
The prostate is a walnut-sized gland that forms part of the male genitourinary tract. It encircles the urethra (tube draining urine from the bladder), sitting below the bladder and in front of the rectum.
The main purpose of the prostate is to produce semen, which helps to protect and nourish sperm.
What are the symptoms of prostatitis?
Symptoms can be variable and sometimes subtle. They include:
- Burning and stinging when passing urine.
- Penile pain, commonly at the tip.
- Lower abdominal/pelvic pain, radiating to inner thighs.
- Testicular/perineal pain (the area between testes and back passage).
- Feeling of ‘sitting on a golf ball’.
- Reduced sex drive (libido)
- Sexual dysfunction (poor erections, pain on ejaculation)
How is prostatitis treated?
Bacteria can be stubborn to clear from the prostate so often a prolonged course of antibiotics (e.g. ciprofloxacin) is required. Some patients have persistent symptoms to varying degrees despite antibiotics. This is often due to persistent inflammation in the prostate, a condition known as chronic prostatitis or chronic pelvic pain syndrome. These symptoms can have a significant impact on quality of life, causing anxieties and stress.
What treatments are available for chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)?
A number of treatment strategies are available such as anti-inflammatories, medication targeting nerve pain, alpha-blockers relaxing muscles around the prostate, PDE-5 inhibitors (e.g. tadalafil) increasing blood flow to the pelvis. Sometimes surgical intervention can help.
Mr Gill will support and guide you through the diagnostic and therapeutic process, tailoring treatment to your individual needs.